Broadcom eCos | Firmware Analysis with Ghidra
In this post I’ll share tools, tips, and tricks to help you reverse engineer an eCos firmware image dumped from a Broadcom eCos BFC cable modem. I consider that you have an extracted firmware image with you and the latest version of Ghidra installed.
If you don’t know how to dump a firmware image, head over to Writing a device profile for bcm2-utils.
Extracting ProgramStore Images
Broadcom use a custom format to store firmware images called “ProgramStore”. This format is composed of a header and then the actual firmware content compressed with one of 5 supported methods of compression. The compression mode is set in the file header.
Broacom released sources related to ProgramStore when they released their bootloader for the Zephyr platform, you can find the code at https://github.com/Broadcom/aeolus.
Let’s take a look at the header definition first:
typedef struct _BcmProgramHeader
{
// the unique signature may be specified as a command
// line option: The default is: 0x3350
unsigned short usSignature;
// Control flags: currently defined lsb=1 for compression
// remaining bits are currently reserved
unsigned short usControl;
// Major SW Program Revision
unsigned short usMajorRevision;
// Minor SW Program Revision
// From a command line option this is specified as xxx.xxx
// for the Major.Minor revision (note: Minor Revision is 3 digits)
unsigned short usMinorRevision;
// calendar time of this build (expressed as seconds since Jan 1 1970)
unsigned long ulcalendarTime;
// length of Program portion of file
unsigned long ulTotalCompressedLength;
// Address where program should be loaded (virtual, uncached)
unsigned long ulProgramLoadAddress;
// NULL terminated filename only (not pathname)
char cFilename[48];
// For future use
char pad[8];
// When doing a dual-compression for Linux,
// it's necessary to save both lengths.
unsigned long ulCompressedLength1;
unsigned long ulCompressedLength2;
// 16-bit crc Header checksum (CRC_CCITT) over the header [usSignature through cFilename]
unsigned short usHcs;
// reserved
unsigned short reserved;
// CRC-32 of Program portion of file (following the header)
unsigned long ulcrc;
} BcmProgramHeader;We can visually represent this structure as follows:
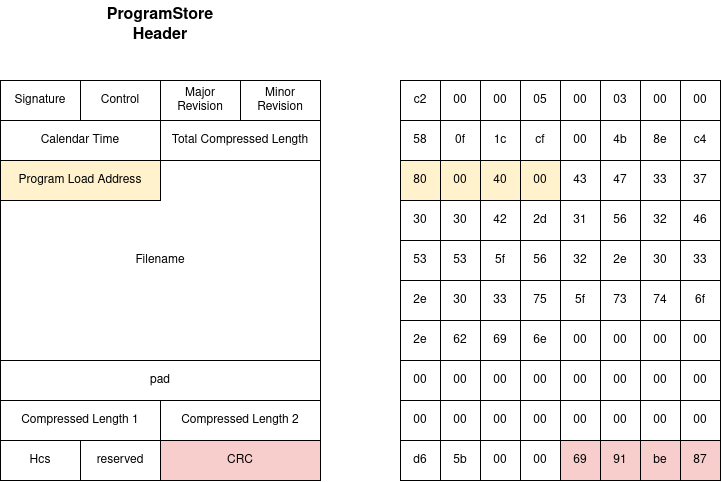
Using the ProgramStore utility, it’s easy to decompress the actual firmware from a ProgramStore file:
./ProgramStore -x -f TCG300-D22F.EG00.15.01.OBE.01.05.11-V-E-170630_sto.bin
Signature: d22f
Control: 0005
Major Rev: 0100
Minor Rev: 01ff
Build Time: 2017/6/30 12:17:00 Z
File Length: 5258252 bytes
Load Address: 80004000
Filename: TCG300-D22F.EG00.15.01.OBE.01.05.11-V-E-170630_sto.bin
HCS: d1d8
CRC: 35948d51You can then import the resulting file into Ghidra.
Loading firmware in Ghidra
All the Broadcom based eCos cable modems runs MIPS 32bit big endian chipsets, so you can set the target architecture to that without hesitation. You also have to set the right load address, which we read from the ProgramStore file header (here it’s 0x80004000).
Applying FunctionID
Ghidra provides an interesting feature called FunctionID. It is similar to what IDA provides under the FLIRT name or Binary Ninja “Signature Libraries”.
I won’t go into the details but basically it will compute instruction patterns of each function you have currently defined in the binary you’re analyzing and save these patterns in a database. When you load another binary, you can run FunctionID which will execute pattern matching against all functions and rename them accordingly.
If you want to dig deeper into the subject I recommend you go to Hex Ray’s blog and specifically read IDA F.L.I.R.T. Technology: In-Depth.
Ideally, what we want is a database of patterns matching all the eCos standard library functions. To generate such a database, we will follow these steps:
- Download the eCos source code
- Cross-compile each eCos subsystem to a MIPS32 big endian ELF object files
- Load all object files to a dedicated Ghidra project subdirectory
- Run FunctionID analysis on all loaded object files
- Export the FunctionID database
The FunctionID auto-analysis is largely inspired by threatrack’s work at https://blog.threatrack.de/2019/09/20/ghidra-fid-generator/
Downloading eCos Source Code
While eCos sources can be downloaded from their original repositories, two cable modem vendors (Technicolor and Netgear) released the specific versions they use in order to honor the GPL.
There is exactly no differences whatsoever between the code released by these vendors. It’s eCos version 2.0 with three different profiles: BCM33 chipsets, BCM33 chipsets with IPv6 support, BCM33 chipsets with SMP support.
You can take a look yourself by checking out these sources:
So we can assume that the Broadband Foundation Classes provided by Broadcom under the “BFC” name are all based on eCos version 2.0. The standard eCos packages and libraries will therefore be the same between every firmware that is built for Broadcom chipsets.
The eCos license allows commercial users of eCos not to release the code they built on top of eCos so we will miss the actual BFC libraries that are closed source.
Cross-compilation of shared object files
Getting the proper toolchain to build eCos is a real pain. The instructions are clear but they are based on quite old software tools. I finally managed to get everything right by doing everything on a Centos box using Vagrant.
Vagrantfile
Vagrant.configure("2") do |config|
config.vm.box = "generic/centos6"
config.vm.hostname = "ecos-toolchain"
config.vm.provision "shell", path: "setup.sh", privileged: false
endsetup.sh
#!/bin/sh
TARGET="mipsisa32-elf"
PREFIX="${HOME}/gnutools"
mkdir -p ${PREFIX}
mkdir -p /tmp/src
echo "[+] Installing dependencies."
sudo yum install -q -y compat-gcc-34 binutils glibc-devel.i686 tcl unzip
echo "[+] Downloading sources."
wget --quiet ftp://ftp.gnu.org/gnu/gcc/gcc-3.2.1/gcc-core-3.2.1.tar.gz
wget --quiet ftp://ftp.gnu.org/gnu/gcc/gcc-3.2.1/gcc-g++-3.2.1.tar.gz
wget --quiet ftp://ftp.gnu.org/gnu/binutils/binutils-2.13.1.tar.bz2
wget --quiet ftp://ftp-stud.fht-esslingen.de/pub/Mirrors/sourceware.org/newlib/newlib-1.11.0.tar.gz
wget --quiet https://ftp.gnu.org/gnu/gcc/gcc-3.4.6/gcc-3.4.6.tar.gz
echo "[+] Downloading patches."
wget --quiet https://ecos.sourceware.org/binutils-2.13.1-v850-hashtable.patch -O /tmp/src/binutils-2.13.1-v850-hashtable.patch
wget --quiet https://ecos.sourceware.org/gcc-3.2.1-arm-multilib.patch -O /tmp/src/gcc-3.2.1-arm-multilib.patch
tar xzf gcc-core-3.2.1.tar.gz -C /tmp/src
tar xzf gcc-g++-3.2.1.tar.gz -C /tmp/src
tar xzf gcc-3.4.6.tar.gz -C /tmp/src
tar xf binutils-2.13.1.tar.bz2 -C /tmp/src
tar xzf newlib-1.11.0.tar.gz -C /tmp/src
cd /tmp/src
echo "[+] Applying patches."
patch -p0 < binutils-2.13.1-v850-hashtable.patch
patch -p0 < gcc-3.2.1-arm-multilib.patch
echo "[+] Moving newlibs."
mv newlib-1.11.0/newlib gcc-3.2.1 > /dev/null 2>&1
mv newlib-1.11.0/libgloss gcc-3.2.1 > /dev/null 2>&1
echo "[+] Building binutils 2.13.1."
mkdir -p /tmp/build/binutils
cd /tmp/build/binutils
/tmp/src/binutils-2.13.1/configure --target=${TARGET} --prefix=${PREFIX}
make -w all
make install
echo "[+] Building GCC 3.4.6"
mkdir -p /tmp/build/gcc-3.4.6
cd /tmp/build/gcc-3.4.6
/tmp/src/gcc-3.4.6/configure --prefix=${PREFIX} --enable-languages=c,c++ --with-gnu-as --with-gnu-ld
make -w all
make install
export PATH="$PATH:${PREFIX}/bin"
export gcc="${PREFIX}/bin/gcc"
export CC="${PREFIX}/bin/gcc"
echo "[+] Building GCC 3.2.1."
mkdir -p /tmp/build/gcc
cd /tmp/build/gcc
/tmp/src/gcc-3.2.1/configure --target=${TARGET} --prefix=${PREFIX} --enable-languages=c,c++ --with-gnu-as --with-gnu-ld --with-newlib --with-gxx-include-dir="${PREFIX}/${TARGET}/include" -v
make -w all
make install
echo "[+] Cleaning up."
cd
rm -f *gz
rm -f *bz2
rm -rf /tmp/src
rm -rf /tmp/build
echo "[+] Done"
cd
export PATH="$PATH:${HOME}/gnutools/bin"
echo "[+] Downloading eCos source."
wget --quiet "https://www.downloads.netgear.com/files/GPL/CG3700B_v5.5.7mp2_LxG1.0.7mp2_src.zip"
unzip CG3700B_v5.5.7mp2_LxG1.0.7mp2_src.zip
unzip CG3700B_v5.5.7mp2_LxG1.0.7mp2_src/CG3700B_v5.5.7mp2_src.zip
tar xvf CG3700B_v5.5.7mp2_src/ProdD30_BFC5.5.7mp2_eCos.tar.bz2
# fix tail call syntax
find -name "build.bash" -print -exec sed -i "s/make -s clean/find -iname \"make*\" -exec sed -i \'s\/tail \+2\/tail -n\+2\/g\' \{\} \\\;\nmake -s clean/" {} \;
# remove unnecessary call to diff
find -name "build.bash" -print -exec sed -i 's/^diff.*$//' {} \;
echo "[+] Building bcm33xx."
cd ${HOME}/rbb_cm_ecos/ecos-src/bcm33xx
bash build.bash > /dev/null 2>&1
echo "[+] Done."
echo "[+] Building bcm33xx_smp."
cd ${HOME}/rbb_cm_ecos/ecos-src/bcm33xx_smp
bash build.bash > /dev/null 2>&1
echo "[+] Done"
echo "[+] Building bcm33xx_ipv6."
cd rbb_cm_ecos/ecos-src/bcm33xx_ipv6
bash build.bash > /dev/null 2>&1
echo "[+] Done"
mkdir -p /tmp/ecoslibs
find -name "*.o" -print -exec cp {} /tmp/ecoslibs/ \;
FUNC_TOTAL=`find /tmp/ecoslibs -name "*.o" -exec mipsisa32-elf-objdump -t {} \; | grep F | awk '{ print $6}' | sort -u | wc -l`
echo "[+] ${FUNC_TOTAL} functions ready to be translated into FIDB."
echo "[+] Object files are now available in /tmp/ecoslibs."Once everything is done, you’re left with a bunch of .o files that we can import into Ghidra.
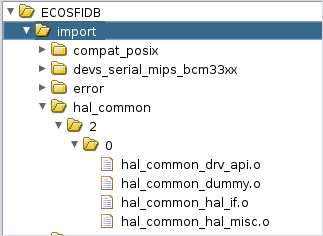
For the next steps, I’ll be relying on scripts developed by Threatrack to auto-import and auto-generate FIDB files. These scripts expect the imported files to follow a specific structure (root/library_name/version/variant/file.o).
I developed the Python script below to move and rename files around so that our generated eCos object files would follow this naming scheme.
#!/usr/bin/env python3
import glob
import os
import shutil
root="/tmp/sorted"
version="2"
variant="0"
#os.rmdir(root)
os.makedirs(root, exist_ok=True)
for name in glob.glob("**/*.o", recursive=True):
library_path = name.split("v2_0")[0][0:-1]
elf_name = name.split("/")[-1]
library_name = library_path.replace("/", "_")
dest_dir = dest = "{}/{}/{}/{}".format(root, library_name, version, variant)
dest_file = "{}/{}".format(dest_dir, elf_name)
os.makedirs(dest_dir, exist_ok=True)
print(dest_file)
shutil.copy2(name, dest_file) # complete target filename givenThe result once imported:
Auto-import and analysis of shared object files
Here I’m relying on two scripts from threatrack.
#!/bin/sh -x
GHIDRA_HOME="${HOME}/ghidra_9.1.2"
GHIDRA_PROJ="${HOME}/reversing"
GHIDRA_HEADLESS="${GHIDRA_HOME}/support/analyzeHeadless"
PROJECT_NAME="ECOSFIDB"
SOURCE_DIR="/tmp/sorted"
LANG_ID="MIPS:BE:32:default"
rm -rf fidb
mkdir -p fidb
echo '' > ecos-common.txt
echo '' > duplicate_results.txt
echo "[+] Importing files from ${SOURCE_DIR} into project ${PROJECT_NAME}."
echo "[+] Running auto-analysis (this can take some time)."
${GHIDRA_HEADLESS} ${GHIDRA_PROJ} ${PROJECT_NAME} -import ${SOURCE_DIR} -recursive -preScript FunctionIDHeadlessPrescript.java -postScript FunctionIDHeadlessPostscript.java -processor ${LANG_ID}
echo "[+] Packing into FIDB"
"${GHIDRA_HEADLESS}" "${GHIDRA_PROJ}" "${PROJECT_NAME}" -noanalysis -preScript AutoCreateMultipleLibraries.java /tmp/duplicate_results.txt true fidb "broadcom-ecos.fidb" "/sorted" /tmp/ecos-common.txt "${LANG_ID}"
echo "[+] Done."After all these steps we’re left with a FIDB file holding 2180 function signatures spanning 26 standard libraries. This will be super helpful during our analysis process.
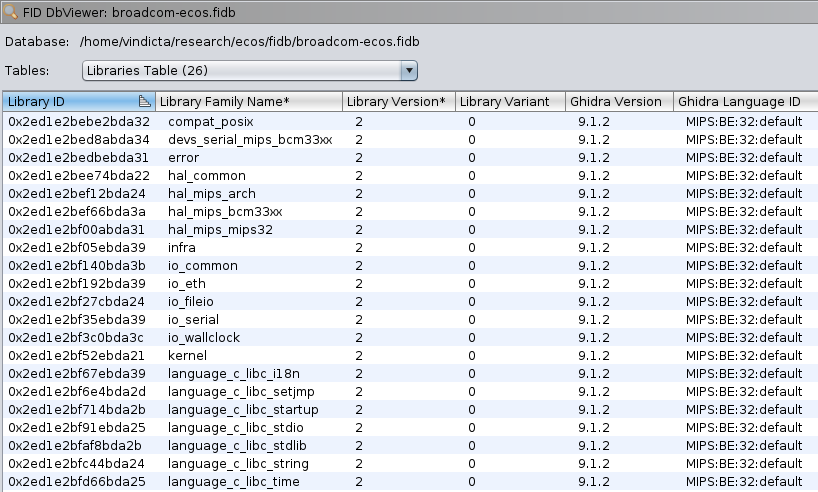
The FIDB can be downloaded here.
Setting Up Memory Mappings
The first step is to identify the different memory regions using the script we developed when we reverse engineered the eCos memory layout.
python3 memory_layout.py firmware.bin
.text start: 0x80004000
.text end: 0x80f20ec8
.text length: 0xf1cec8
.data start: 0x80f20ecc
.data end: 0x811d205c
.data length: 0x2b1190
.bss_start: 0x81979f48
.bss_end: 0x81bc89a0
stack start: 0x81a7ca48
stack end: 0x81a80a48Click on ‘Window’ -> ‘Memory Map’, select the RAM line and click on ‘Split’ icon.
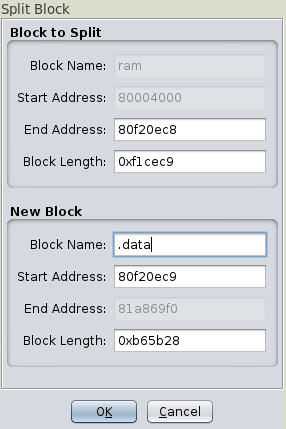
Here we split RAM in two regions: .text (code) and .data (data):
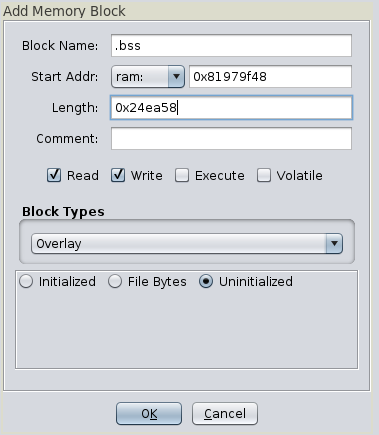
Once that’s done, we can add new regions. We can add the BSS as an overlay:
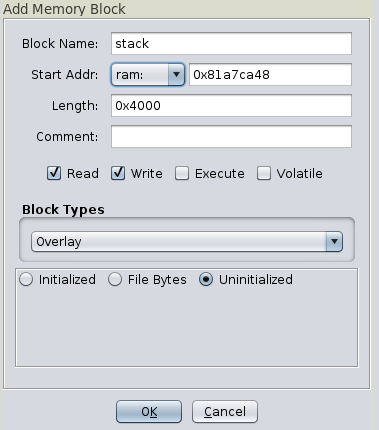
The stack, also as an overlay:
You can define locations of vectors related to interrupt and exception handling:
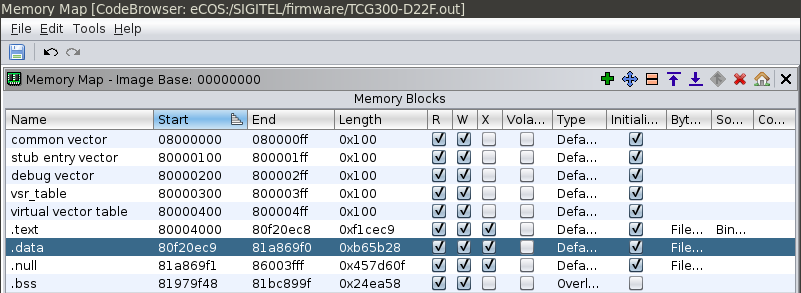
This should be what you’re left of with:
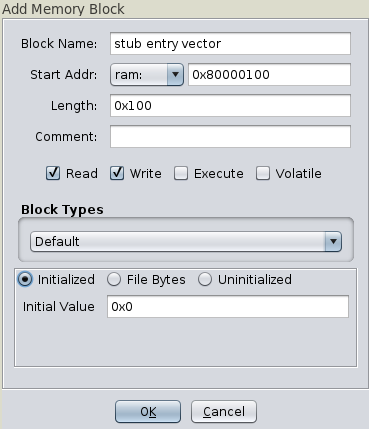
A nice addition would be to dump the section from 0x80000000 to 0x80004000 and append it to our image, in order to get exception and interrupt handlers in our analysis view.
Automated Function Renaming
When reversing my first firmware images, I identified tracing functions left by Broadcom. The first one logs a message in the form -<%s>-\t Entering func \n with the function name it’s called from as first parameter.
This means we could trace all calls to that function and use the third argument to effectively rename the function it’s called from:
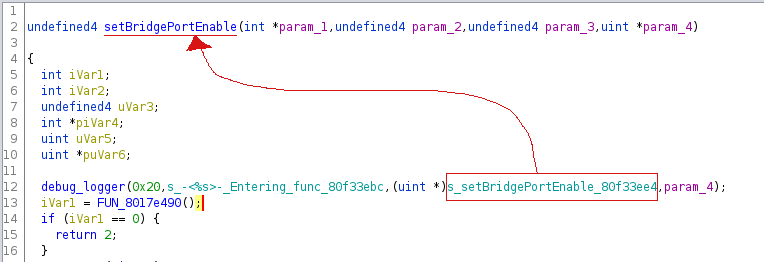
Two other functions are called almost always in pairs. The first one logs the function name while the other logs “Entering” or “Leaving” then the function name:

The third one I identified seems to set these strings into the C++ class definition.
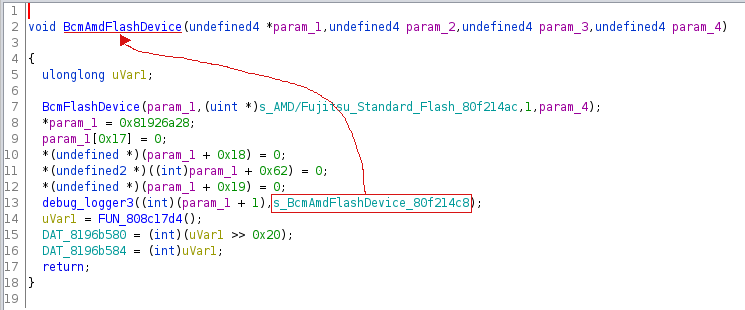
Similar conventions were observed for other logging functions:

To take advantage of that, I wrote a custom Ghidra script that given a logging function would:
- get a list of all functions calling that logging function (cross-references)
- for each call, get the pointer value that is put into $a1, $a2, or $a3 depending on the logging function parameters
That script is available on its dedicated repository
Some stats on current projects:
- ASKEY: 54667 functions identified by Ghidra, 3179 auto-renamed with the script, 1972 identified with eCos FIDB (5151 functions identified, which is close to 10% of the binary that was identified).
- Netgear: 50138 functions identified by Ghidra, 2603 auto-renamed with the script, 1972 identified with eCos FIDB (4575 functions identified, which is close to 10% of the binary that was identified).
Automated VTable Identification
By looking at the function names observed in logging calls, we see the “classname::function_name” nomenclature, which indicates usage of C++.
If you look at constructor functions - considering you set the function calling convention to “this call” - you’ll see the this pointer set to a specific address:
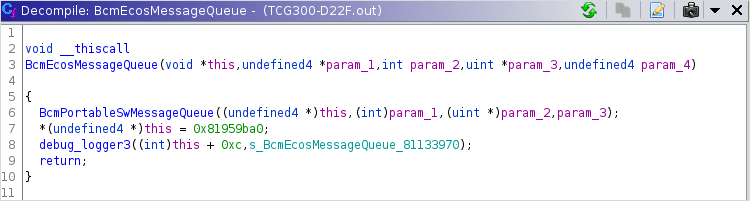
That address is the class virtual table, which holds pointers to the class functions:
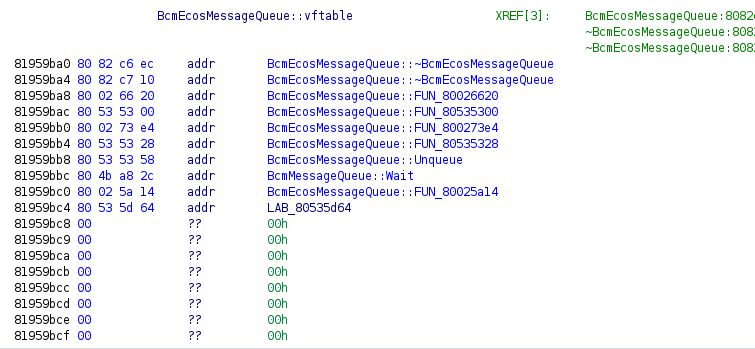
In the screenshots, everything is already named right but this is actually the work of another Ghidra script that I wrote. The script goes over all the ‘PTR_FUN’ labels and checks the function name, if the function name follows the C++ naming convention, it will rename the label to class_name::vftable.
This is super helpful because now we have even more context such as inheritance and implementation of classes. On top of that we can derive other function names based on the structure of the class that implements it.
An excellent example are all the NonVolSettings classes that implements specific sections of nonvol settings. Each of these classes follows pretty much the same structure with WriteTo, ReadFrom, ReadFromImpl and WriteToImpl functions. Even if a class that inherits from NonVolSettings did not implement verbose logging calls, we still can derive its function names given that we know the structure of other NonVolSettings classes vtables.
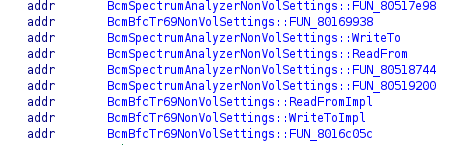
Importing Data Structures from C Headers
Theoretically, you could import data structures from C headers coming from the eCos source code. However, I don’t think this brings a lot of added value at the moment. This would only concern standard library function calls, and would not help you with custom code coming from either Broadcom or the vendor they partnered with. I think it’s more efficient to check the eCos doc whenever you’re tracing such a call than go through the painful process of importing these structures. On top of that, Ghidra does not support having multiple names for the same data type (as in, multiple typedefs call), which pretty much leads to losing all context.
Conclusion
In this article we demonstrated how to properly extract and load a ProgramStore image into Ghidra, set memory mappings, and perform auto-identification of functions and classes by taking advantage of Ghidra scripting capabilities.
My final objective with this is to implement a complete Ghidra loader that would execute all these actions in one go, but I still have to find the time to do that.
At this point, all that is left from a vulnerability research perspective is to identify dangerous function calls (using Rhabdomancer for example), and work your way from there by using the context gained from the automated renaming scripts. The heavy lifting is done, now all you have to do is rename or re-type a few things here and there to get the bigger picture.
As always, if you have any question feel free to contact me via Twitter or email.
Tagged #ecos, #reversing, #ghidra, #broadcom.